Wastewater Treatment
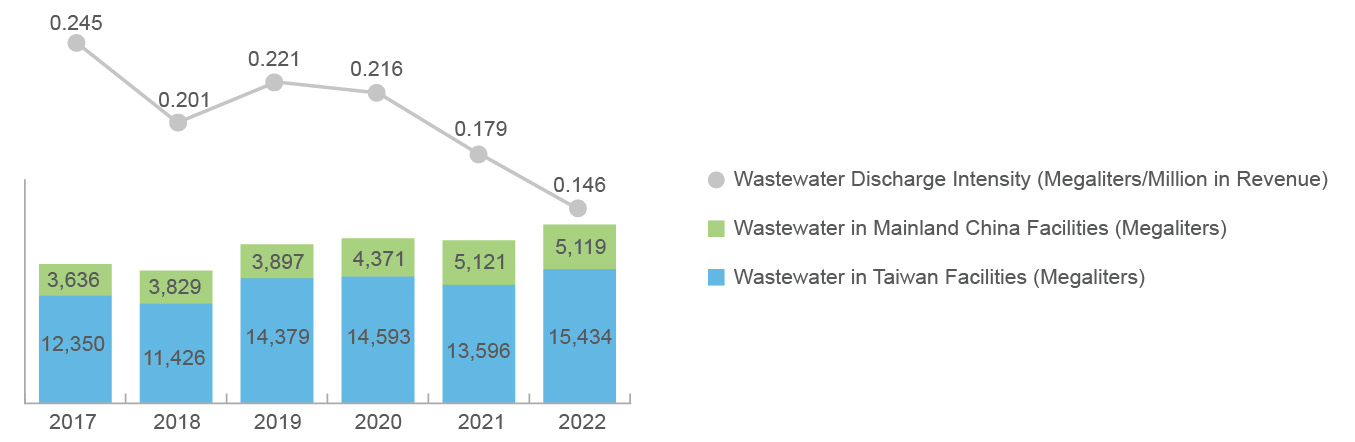
Total wastewater discharge in 2022 was approximately 20,554.080 megaliters, an increase of 10% compared to 2021, and a decrease of approximately 18% in discharge intensity per unit of revenue. In 2022, wastewater discharges from the plants in Taiwan and China were approximately 15,434 megaliters and 5,120 megaliters, accounting for 75% and 25% of total discharges, respectively. The wastewater discharged from Unimicron's operating sites has been treated at wastewater facilities and confirmed to meet discharge standards before being discharged into designated streams or incorporated into local wastewater treatment plants.
After treatment, the wastewater from our plants in Taiwan will be legally discharged into the streams and incorporated into the local sewage treatment plants, including Nankan River, Laojie River, Dongmen River, and Xinfeng River. The wastewater from our plants in Mainland China is discharged to the local exclusive sewage treatment plants, and after treatment, they are finally legally discharged to Maozhou River, Wusong River, and Taicangtang. The right to water is an indispensable right for the realization of human dignity life and health. The wastewater from the plants in Taiwan and China is discharged after treatment and will not pose a threat to the ecology of the local watersheds or natural water bodies, nor will it have any negative impacts on the local communities access to safe drinking water.
In order to eliminate the stigma of the high-pollution industry of printed circuit boards, we have established strict internal control standards for wastewater discharge "Environmental Protection Internal Audit and Notification Operation Measures", and complied with local regulations and requirements "Water Quality Standards for Discharged Water from the Printed Circuit Board Manufacturing Industry." Taking Hsinfeng Plant as an example: The internal control standard of chemical oxygen demand is 108ppm, with the regulatory standard being 120ppm, and the copper internal control standard is 1.2ppm, with the regulatory standard being 1.5ppm. At present, the discharge levels of plants in both Taiwan and China are far below the approved standards of local regulations (the permissible value of chemical oxygen demand is 4.19 megaliters, and the permissible value of copper is 0.19 megaliters), and the wastewater quality is in compliance with the discharge standards of the relevant local laws and regulations. We publish quarterly testing data on wastewater discharge by third-party and disclose the wastewater treatment process in the below section. In response to the stricter revision of wastewater discharge standards in the environmental protection laws in the future, the plants in Taiwan have evaluated the performance of the existing wastewater treatment facilities and the current treatment can meet the future discharge standards. To avoid the impacts of stricter environmental protection regulations in the future, we will continue to reduce source pollutants and develop internal wastewater discharge control standards that are superior to laws and regulations to reduce pollution.
Wastewater Discharge and Intensity
Note: The wastewater from the plants in Taiwan is discharged to surface water and local wastewater treatment facilities, and the wastewater from the plants in mainland China is discharged to local wastewater/treatment facilities.
Reduction Projects and Results
Wastewater diversion into biological treatment,Increase capacity of wastewater plants,Reduce energy consumption of subcontracted processing
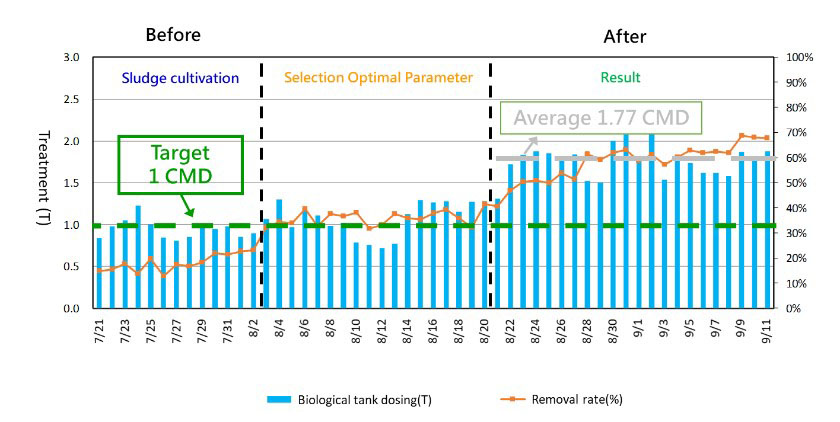
In addition tothe production of copper-containing waste liquid in the printed circuit board manufacturing industry, film-removing waste liquid also accounts for a large amount. The company's wastewater treatment process adopts a chemical coagulation system, which is mainly used for the treatment of copper-containing waste liquid, and its ability to treat COD is poor. In the past, the treatment method of film-removing waste liquid was to pass the waste liquid through the aeration and stratification system, and then outsource the high-concentration film-removing waste liquid; the low-concentration waste liquid was discharged into the waste water plant for self-treatment. When the company's production capacity increased, the waste liquid When the treatment capacity reaches the load of the wastewater plant and cannot continue to stratify, the stock solution will accumulate and need to be cleared and transported by outsourcing, which will increase the cost of outsourcing treatment. The company's 2020 project introduced the method of contacting biological filter materials, using biofilms to treat COD in water under an aerobic state, and successfully increased the capacity of waste water plants to treat COD waste liquid, increasing 1.77 tons per day, and a total of 53.1 tons per month. Reduce the cost of outsourced cleaning and transportation, increase the capacity of the wastewater plant to treat COD waste liquid, and avoid the discharge of COD-containing wastewater into the environment to increase the environmental load and affect the ecological environment.

Waste Water Quality Monitoring
order to monitor the water quality at any time, set up a continuous monitoring system and connect with theEnvironmental Protection Administration to monitor the water temperature, pH, conductivity, COD, and SS in real time.