Water Resources Management
Limited by the industry’s characteristics of relying on stable water resources, water source and volume have become one of the most important keys to the continued operation of Unimicron. There are significant differences in rainfall and flow volume in the current high-water period and low-water period in Taiwan, and many meteorological and hydrological extremes have occurred. In response to the risk of a water shortage caused by Taiwan's topography and climate change, the use and retention of water resources had been evaluated at the initial stage of establishing each of Unimicron's facilities. Not only set up Storage tanks but the water storage capacity of each regional reservoir and the water consumption status of each plant is monitored and managed during normal times to ensure that the plant does not have an immediate water shortage crisis due to lack of water resources, and the ability to withstand water shortages is improved.
 Achieved Platinum Certification from the AWS (Alliance for Water Stewardship Standard)
Achieved Platinum Certification from the AWS (Alliance for Water Stewardship Standard)
In order to effectively manage water resources and reduce environmental and ecological impacts, as well as to keep enhancing the efficiency of water use, Shanying Plant became the first to utilize the AWS International Water Stewardship Standard in 2020 and has been certified by a third party to have achieved Platinum status. By adhering to Green Ecology, Green Competitiveness, and Green Humanity, our three environmental values, we have been practicing sustainable and systematic water management, and have demonstrated five major achievements.
- Good water management system: Comprehensive personnel training mechanism, comprehensive and effective procedures
- Sustainable water balance: Open and quantifiable water efficiency targets and current status, continuous improvement and enhancement of water efficiency
- Excellent water quality: Independent and effective testing and monitoring, stable water discharge quality that is superior to regulation quality
- Health of important drainage areas: Environmental education for critical drainage areas helps environmental awareness take root
- Safe water, environment and personal hygiene: Provision of a safe, hygienic environment and drinking water for people at the plant
In response to the challenges of climate change and resource scarcity in the future, every drop of water that comes into, is used by, and leaves our plant is cherished as well as effectively and precisely managed in an environmentally friendly way so that we can move towards sustainability goal of zero water waste.
All of Unimicron’s plants are not located in areas with frequent water shortages and drought, and the main water source is tap water. Unimicron’s Taiwan Facilities still use well water and rainwater. However, because it is not easy to collect information about the impact of well water and rainwater, the assessment was not included this year. In 2022, the water consumption of each plant accounts for a small proportion of the water supply in the water intake area, and there was no significant impact on the water intake area (>5% of the water supply in the intake area is a significant impact).
Water Assessment Results
Upstream
Unimicron
Downstream (Packaging)
- Increase in the quantity of water discharge
- Heavy metals in the discharged water
- Large quantity of water intake
- Large quantity of water discharge containing heavy metal
The downstream manufacturers are packaging plants, which are not highly water-consuming industries, and thus it is judged to have no impact
- Legal compliance
- Water and soil pollution, biodiversity, and human health
- Conflict of interest with stakeholders in shared water resources
- Water and soil pollution, biodiversity, and human health
The downstream manufacturers are packaging plants, which are not highly water-consuming industries, and thus it is judged to have no impact
- Obtain discharge permits issued by local governments under the law and complete reporting
- Implement wastewater treatment and discharge water monitoring management, reducing the impact of pollution in the watershed
- Monitor the water use situation in the plant and back up the water supply from other sources. Reduce water resource consumption by recycling water for production. Communicate with stakeholders in times of water shortage
- Use water discharge monitoring and management to effectively reduce the impact of pollution in the watershed
The downstream manufacturers are packaging plants, which have no impact on water intake/discharge, and it is judged to not need mitigation measures
Water Resource Dispatching Measures in Taiwan Facilities
There was no emergency event activated due to water issues in 2022 but we still establish contingency measures for water resources dispatch for drought periods. We actively carry out water resources standardization and management through the tracking of regime lights. The emergency response water dispatch team is in charge of water trucks, water tanks, water sources, and other matters regarding water resources dispatching, to ensure uninterrupted operations.
Drought Monitoring Signal
Government Measures
Unimicron’s Contingency Plan
Stable Supply
Water monitoring in various regions/water use management in each plant
Agricultural fallow
Establishing an emergency water scheduling team/drawing up an emergency water plan
Decompression of water supply at a specific time
Responding by water saving in production/water trucks/responding by reserving water source backup
Reduced supply of industrial water
Emergency response water scheduling team operation/implementing water restriction response measures at various stages
Suspended water supply by zone and time slot
Emergency response water scheduling team operation/implementing water restriction response measures at various stages
Water Resources Use
In 2022, the proportion of water resources used by the plants in Taiwan accounted for about 71.7%, and they were 4.6% for the plants in South China, and 23.7% for the four plants in East China/Central China. The total water intake volume in 2022 was 21,340.80 megaliters, rainwater only accounted for 0.03%, well water and tap water accounted for 23% and 76.7% of the total water intake volume, respectively. The average usage of well water in the past two years was about 5,041 megaliters, and the average usage of tap water in the past two years was about 15,642 megaliters. 7.03 megaliters of rainwater were recycled in 2022 to replace tap water for watering landscaping, etc. We hope to achieve the function of water conservation and distribution by storing and utilizing rainwater. In terms of the total water intake intensity per unit of revenue, there was a decreasing trend in the last five years, with a reduction of about 21% in 2022 compared to 2021, which is a significant improvement in water intake efficiency.
Water Withdrawal and Intensity
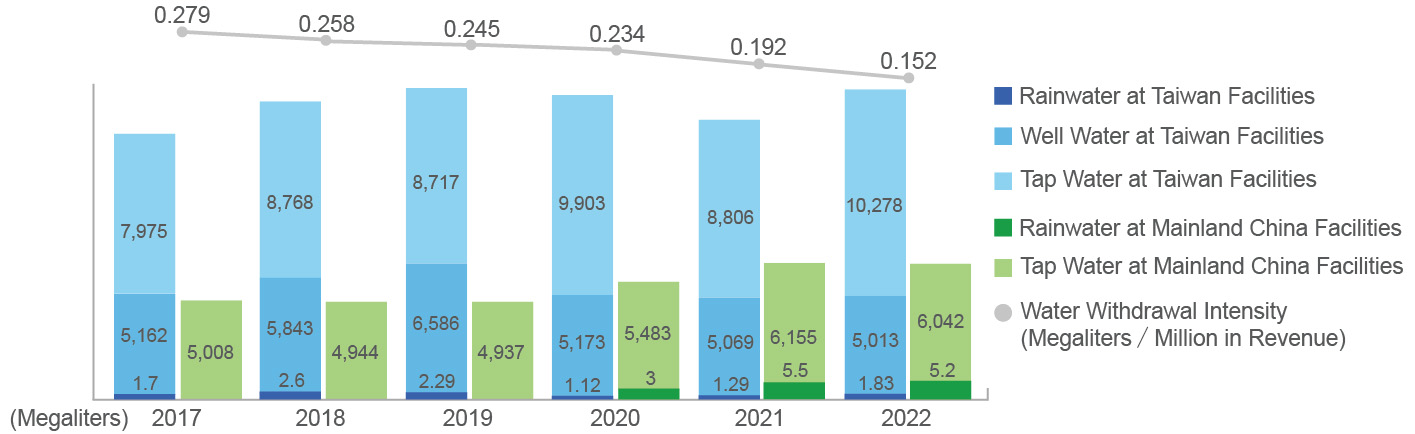
Note 1: The above information does not include the Nanshan plant.
Note 2: The water sources of the Kunshan and Suzhou plants are Yangcheng Lake and Taihu Lake, and the water sources of the Shenzhen plant are Songgang Wuzhipa Reservoir.
Note 3: Calculation method of rainwater recovery: average annual rainfall in each region × catchment area.
Note 4: The definition of Groundwater is a depth of over 700 meters.
Note 5: Rainwater and well water are surface water and tap water is a third-party supply.
Water Resources
(Unit: Megaliters)
Note: Freshwater is the source of intake and discharge.
Unimicron’s Annual Water Intake Volume as a Percentage of
the Water Supply District’s Annual Intake Volume
(Unit: %)
Note 1: The data source is the "Statistics of Water Intake from Reservoirs and Weirs” of the Northern Region Water Resources Office, WRA, MOEA, and the water intake is the average total for the last five years.
Note 2: The source of water supply for the plants in Taoyuan is Shimen Reservoir. The water intake from the reservoir includes Taoyuan Dazun (Taoyuan Irrigation Association), Taoyuan Dazun (Water Supply Corporation, etc.), Shimen Dazun (Shimen Irrigation Association), and Shimen Dazun (Water Supply Corporation, etc.).
Note 3: The source of water supply for the plants in Hsinchu is the Lung-En Weir catchment area, and the regional water intake includes Lung-En Weir (Water Supply Corporation) and Lung-En Weir (Lung-En-Zun irrigation area).
Note 4: The ratio of Unimicron’s annual water intake to annual water intake in the water supply area = annual tap water consumption of the plants in the area/annual average total water intake in the regional water supply area×100%.
Water Recycling
Cause of climate change, climatic characteristics such as temperature and rainfall will change. In addition to increasing temperature, rainfall may be unevenly distributed in time and space. For example, the increase in rainfall during the high-water period and the decrease in the rainfall during the low-water period have led to a larger monthly difference in river flow, which may further lead to an imbalance in the water supply and demand system. Unimicron continuously improves water-saving to increase water efficiency and rainwater recovery storage tanks are installed in each plant to reduce water consumption. In addition, we continuously add water-recycling systems to reduce the consumption of water resources by recycling low-polluting water sources produced in various processes and treating them to replace the water used for industrial production. The recycling rate of water resources in 2022 was 29% (6,204 megaliters), and the average recycling rate in the past two years was 28%.
Water Resource Recovery Ratio
(Unit: %)
Note 1: Recovery rate (%): Total water recovered/Total water consumption.
Note 2: The definition of Water Resource Recovery is reclaimed water.
2022 Water Conservation Program
We value water resource management, and water resources play an important role in the PCB industry. In 2022, we renew the "production process" and "equipment" to improve water efficiency and water recycling, and implement several projects to save 556.8 megaliters of water in 2022.
2022 Water Conservation Projects
Title
Increase water recycling at the flagship plant and move towards the goal of water sustainability.
Content
We continue to add a water recycling system to reduce water consumption by recovering low-pollution water generated in various processes to replace industrial production water after treatment. Every drop of water resources will be taken from the front end, used in the process, and released in the end. We will continue to move towards the sustainable goal of zero water waste through effective and precise management, friendly environment and ecology, and cherishing energy resources.
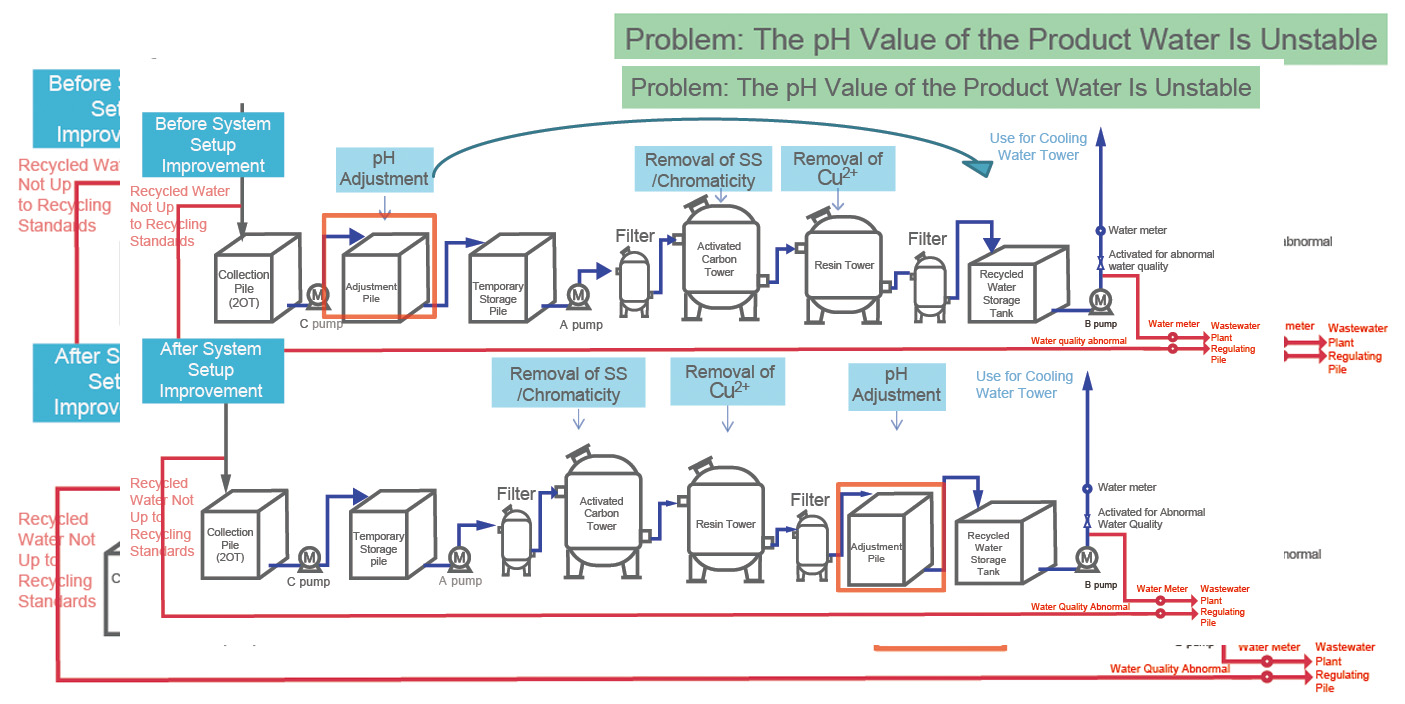
pH Stabilization Improvement Project of Water Recovery System
After the system was built, it was discovered during the test run that the water quality of the effluent into the cooling water tower could not be effectively controlled at pH 6.5~8.5. After discussing with the system equipment supplier, it was confirmed that the activated carbon tower and resin tower will not be affected by the acidity and alkali of the water quality to have any impact on the quality of the water treated. Therefore, we applied the ECRS rule, used the optimized work order of the system to rearrange, changed the pH adjustment tank from the front of the activated carbon tower to the rear of the resin tower, and controlled the quality of the produced water at pH 6.5~8.5 before entering the cooling water tower.
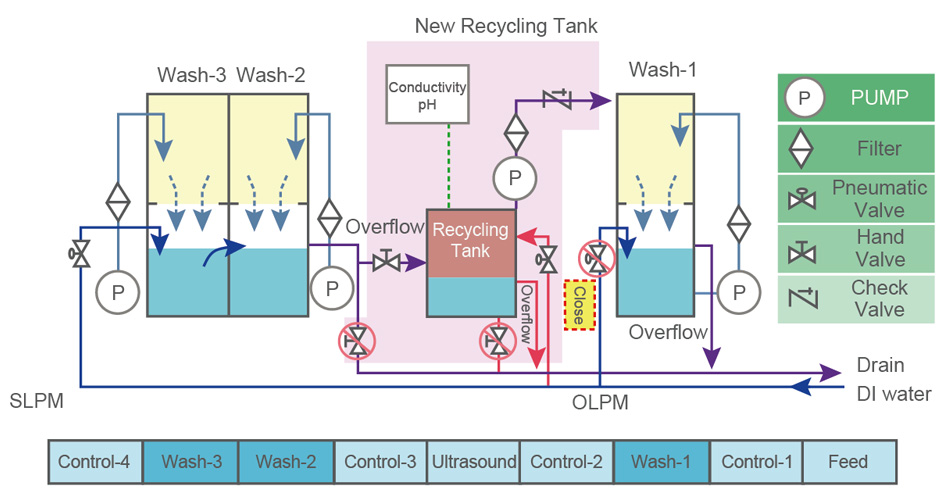
In-Line Water Recycling System
The design principle of the in-line recycling water installation is to use the original overflow water from Wash-2 and return it to the new recycling tank, which is equipped with conductivity and pH monitoring. When the water quality is normal and meets the recovery conditions, the recovered water is pumped/filtered and then used in Wash-1. The new water replenishment in Wash-1 can be turned off.
2022 Achievements
Cost of NT$30 million and water recovery of 947.9 megaliters.




