Climate–Related Risks and Opportunities
Unimicron focuses on global trends related to climate action and has been building a governance framework to incorporate climate change into risk management since 2018, with reference to the Recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures. In 2022, incorporating climate change risk issues into ESG Material Topics and combining them with the Company's business strategy, we developed adaptation and mitigation strategies by analyzing risks and opportunities in the aspects of policies and regulations, market and technology changes, goodwill and entities, and disclosed climate change-related financial information, demonstrating Unimicron's resilience and due responsibilities in the face of climate risks, improving communication with stakeholders, and committing to carbon neutrality by 2050.
Framework
| Framework |
Strategies and Actions |
| Governance |
• Board of Directors: As the highest unit to oversee climate change management, it is responsible for reviewing sustainable management strategies, key guidelines, risk management, annual implementation results, etc.
• ESG Committee: It is served by the Chairperson, executive president and general manager of each business group as members of the committee, and they supervise five sub-committees to set management strategies, goals and specific promotion plans (including climate change-related issues). It regularly reports to the Board of Directors on climate change-related plans and operational results every year. In 2022, a total of 4 climate change-related issues were reported to the Board of Directors.
• Energy Conservation and Carbon Reduction Subcommittee: It is a sub-committee of the ESG Committee, and its main responsibilities include assessing and/or managing climate-related issues, management review of key performance indicators, and setting short-, medium- and long-term goals. The strategies include improving energy efficiency, evaluating the use of renewable energy, carbon emission management, etc., and actively implementing green management effectiveness. |
| Strategy |
• We regard climate action as one of our key corporate missions and integrate it with our core business and operations. We are committed to the introduction and development of various green technologies, actively responding to climate change and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and focusing on the issue of sustainable management of natural resources. Guided by ESG Policy and environmental resources policies, we plan and implement actions to mitigate climate change, focus on global trends related to climate action, and continue to move towards carbon neutrality.
• Identify and assess short-term (1-3 years), medium (3-5 years), and long-term (5-10 years) climate-related risks and opportunities based on the TCFD framework.
• In order to understand the extent to which the Company is impacted by climate change, for those high frequency and high impact items, Unimicron considers the difficulty of obtaining data from common international climate scenario methodologies and applies the Network for Greening the Financial System, using the three scenarios of Net Zeros 2050, Nationally Determined Contributions(NDCs) and Current Policies, to assess the impact of climate change, reduce the operational and financial impact of climate change, and improve organizational climate resilience. |
| Risk Management |
• Relevant departments in the ESG Committee identify risks and opportunities of climate change based on possible issues within their business scope, consider the scope and status of impacts, and perform materiality assessments of entity and transformation risks. The frequency of occurrence and the degree of impact are scored on a five-point scale, with a maximum of five points and a minimum of one point, and ranked according to the score. For items with high frequency of occurrence and high impact, management measures are developed through interdepartmental discussions and the results are reported to the ESG Committee.
|
| Metrics & Targets |
Targets:
- The target of reducing carbon emissions by 8% in 2025 compared to the projected peak.
- The target of reducing carbon emissions by 30% in carbon emissions in 2030 compared to the projected peak.
- The target of achieving carbon neutrality in 2050.
Metrics
Renewable Energy Use:Renewable energy use increases by 30% by 2030.
Greenhouse Gas:The greenhouse gas emission intensity per unit revenue will be kept below 11 in 2023 and below 10 in 2025.
Water Resources:The water consumption intensity per unit revenue will be kept below 300 in 2023 and below 290 in 2025.
Energy Management:The power consumption intensity per unit revenue will be kept below 17 in 2023 and below 16 in 2025.
Waste Management:The waste reuse rate will be maintained above 90% in 2023 and 2025.
Management Mechanisms Relevant emission information has been carried out in accordance with the GHG Protocol and ISO 14064-1 Specification for greenhouse gas inventory, and a third party has been entrusted to verify the data. It continues to promote mitigation measures. Risks Related to Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
Scope 1:The main source of emissions is the natural gas used in boiler steam in the manufacturing process stage. Due to the addition of Shanying II Plant and Yangmei Plant in Taiwan, the increase in usage affects its emissions.
Scope 2:The source of emissions is the emissions generated by purchased electricity, which is mainly related to the emissions from the use of electricity. Due to the addition of Shanying II Plant and Yangmei Plant in Taiwan, the emissions are affected.
Developing Internal Carbon Pricing:Internal carbon pricing is a necessary management tool for the Company to move towards carbon neutrality, and the Company has set the goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. The Company has started to develop a phased introduction of internal carbon pricing to drive active carbon reduction within the Company and reduce external carbon costs.
|
Identification and Assessment of Climate-Related Risks
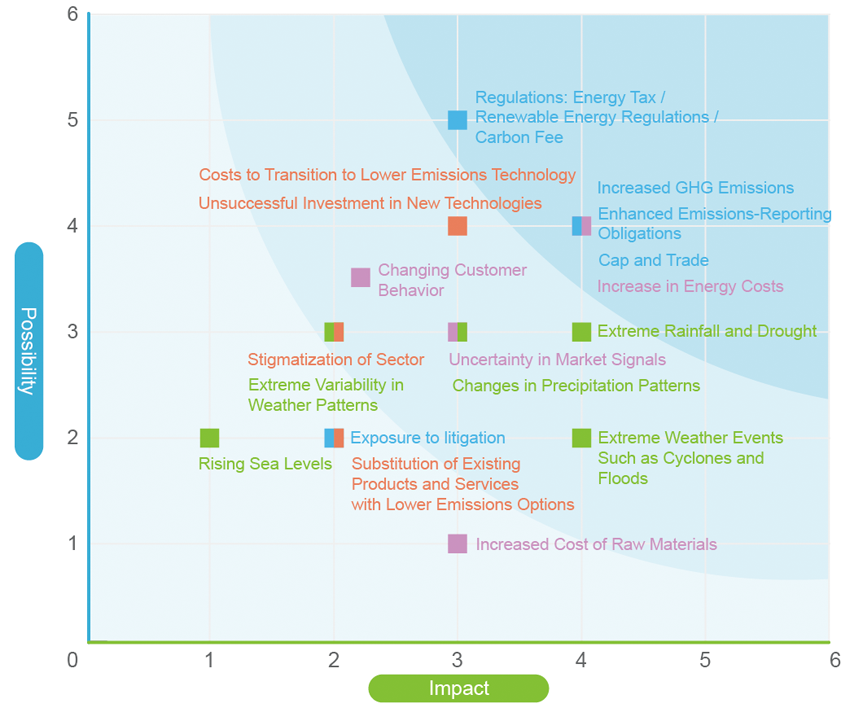
Since 2018, relevant departments of Unimicron's ESG Committee have identified risks and opportunities of climate change based on the issues that may be faced within their business scope. This year, based on the probability of occurrence (5 levels) and the degree of impact (5 levels) of each risk and opportunity, we drew a matrix to grasp major risks and opportunities, to formulate management methods in order to reduce, transfer, or avoid potential impacts.
Risk Identification and Assessment
The results of the matrix analysis of the climate change risk assessment show that there are 5 high transition risks, namely increased GHG emissions, enhanced emissions-reporting obligations, Cap and Trade, increase in energy costs, and Energy Tax / Renewable Energy Regulations / Carbon Fee. There are 5 Medium risks including failure to unsuccessful investment in new technologies, costs to transition to lower emissions technology, uncertainty in market signals, changing customer behavior, stigmatization of sector. The physical risks of extreme rainfall and drought, changes in precipitation patterns, extreme weather events such as cyclones and floods, and extreme temperature changes are the 4 risks in the medium risk category.
Unimicron Climate Change Risk Matrix
Physical Risks
| Item |
Identified Risks |
Period |
Sites |
Level |
Impact |
Strategy |
Potential Financial Impact |
| Acute |
Extreme Rainfall and Drought |
Short-term |
|
Medium |
• Extreme rainfall or drought events may cause abnormal water supply and equipment or supply chain disruptions, resulting in production delays or operational disruptions. |
Regularly monitor water shortage tendencies and develop contingency measures.
The emergency response meeting shall be held during the drought period.
The emergency response water dispatch team is in charge of water trucks, water tanks, water sources, and other matters regarding water resources dispatching, to ensure uninterrupted operations.
|
Reduced revenue from decreased production capacity (e.g., transport difficulties, supply chain interruptions) |
| Extreme Weather Events Such as Cyclones and Floods |
Medium-term |
|
Medium |
• The factory system is damaged, resulting in property loss. |
Flood warning mechanism and emergency response preparation.
Existing plant buildings are equipped with water barriers, the base of the new factory is raised, etc.
Emergency response procedures for natural disasters have been established and will be implemented in stages.
|
| Chronic |
Changes in Precipitation Patterns |
Long-term |
|
Medium |
• Rainfall is mostly concentrated in some areas, leading to water shortages. |
In the use and retention of water resources had been evaluated at the initial stage of establishing each of Unimicron's facilities. Not only set up storage tanks but the water storage capacity of each regional reservoir and the water consumption status of each plant is monitored and managed during normal times.
The emergency response water dispatch team is in charge of water trucks, water tanks, water sources, and other matters regarding water resources dispatching, to ensure uninterrupted operations.
The AWS International Water Stewardship Standard was introduced for sustainable and systematic water management.
Water usage efficiency can be increased in two major aspects: production processes and equipment upgrades.
A project that recycles water from production line equipment improved the water recycling and reuse rate.
|
Increased production costs (Water saving facilities and water recycling systems) |
| Extreme Variability in Weather Patterns |
Long-term |
|
Medium |
• With the rising average temperature in the summer, to maintain the temperature and humidity conditions in the plant, more air conditioning systems need to be turned on to meet the production demand. |
Improve the efficiency of the air conditioning system and add inverters with control, reducing energy use and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Fully use products with energy-saving labels and environmental protection labels.
|
Increased operating costs |
Taiwan Facilities; Mainland China Facilities
Transition Risks
| Item |
Identified Risks |
Period |
Sites |
Level |
Impact |
Strategy |
Potential Financial Impact |
| Policy and Legal |
Increased GHG Emissions |
Short-term |
|
High |
• Greenhouse gas emissions are mainly from electricity consumption. If electricity consumption increases, emissions will increase. |
Continuously grasp the energy efficiency of equipment through the energy management system.
Invest in green electricity and energy-saving and carbon-reducing equipment.
|
Increased operating costs |
| Enhanced Emissions-Reporting Obligations |
Short-term |
|
High |
• Corporate Governance 3.0 blueprint to mandate listed companies to complete GHG inventories of subsidiaries and report emissions information by 2025.
• Investors and customers demand disclosure of carbon emissions information. |
Conducting greenhouse gas inventories.
Disclosing information on the company's official website, annual report, ESG report, the Market Observation Post System and the media.
|
| Cap and Trade |
Medium-term |
|
High |
• Shenzhen City, Mainland China, took the lead in launching carbon emissions trading in June 2013. Unimicron (Shenzhen) began to join the Shenzhen carbon trading mechanism in 2014. As we deal with more stringent carbon caps in the future and a carbon trading market that has grown more sophisticated. If the scale of our operations and production capacity increase in the future, the carbon cost of operation will rise if our quota cannot cover our total carbon emissions.
|
Implement greenhouse gas inventory in accordance with ISO 14064, and continuously monitor and manage to reduce carbon emission intensity.
Continue to expand R&D capabilities, and cooperate with equipment manufacturers and material manufacturers to develop low-carbon technologies.
|
| Regulations: Energy Tax / Renewable Energy Regulations / Carbon Fee |
Medium-term |
|
High |
• Energy Tax: When the Energy Tax is imposed, it will increase the Company's operating expenses.
• Renewable Energy Regulations: Taiwan plants are required by law to install/use renewable energy in accordance with the Renewable Energy Development Act, which will increase the Company's capital expenditure.
• Carbon Fee:
- In the future, Taiwan will impose a carbon fee in accordance with the Climate Change Response Act, which will limit capacity expansion and increase operating costs.
- Installation and operation of carbon reduction equipment, resulting in increased operating costs. |
Energy Tax
Pay attention to changes in regulations and establish response measures in advance to meet regulatory requirements.
Improve energy efficiency through equipment improvement and renewal.
Renewable energy regulations
Plan renewable energy use and evaluate solar photovoltaic facilities based on demand by 2025.
Carbon Fee
Implement inventory and continuous monitoring management to reduce carbon intensity in accordance with ISO 14064 greenhouse gas inventory standards.
Continuously expand R&D capacity and cooperate with equipment and material manufacturers to develop low-carbon technologies.
Set carbon reduction targets, continuously evaluate and plan carbon offset strategies, moving toward carbon neutrality.
Continue to pay attention to the implementation content of laws and regulations.
|
| Technology |
Unsuccessful Investment in New Technologies |
Long-term |
|
Medium |
• Customers may reduce orders because the Company has not met the goals set forth in the regulations and, if necessary, require additional tax payments from the Company. |
For low-carbon products and new product development, the R&D department is responsible for the development of new equipment or new technologies, and reports the progress and work results to the senior executives every week.
|
R&D expenditures in new and alternative technologies |
| Costs to Transition to Lower Emissions Technology |
Medium-term |
|
Medium |
• Invest in hydrogen fuel cells for power generation, increasing operating costs |
Set up hydrogen fuel cells
|
| Market |
Increase in Energy Costs |
Short-term |
|
High |
• Electricity prices are increasing year by year, and the cost of obtaining energy is increasing
• In response to the government's 2050 net zero target, and the proportion of renewable energy will reach 60%-70% by 2050
• The cost of green electricity is higher than that of general electricity |
Improve energy use efficiency
Look for renewable energy suppliers
Use renewable energy and set renewable energy promotion goals
|
Increased production costs due to changing input prices (e.g., energy, water) and output requirements (e.g., waste treatment) |
| Uncertainty in Market Signals |
Medium-term |
|
Medium |
• Because of the uncertainty of global or regional market information, especially in relation to climate change issues, it is difficult to grasp the future market demand for products or services |
Low carbon emission business operation model has been a global consensus. Although it is a customized product, we can still integrate low carbon materials and promote low carbon emission technology at the development stage, and at the same time cooperate with relevant units of the Group to build a low carbon supply chain
|
Change in revenue mix and sources |
| Changing Customer Behavior |
Medium-to-long term |
|
Medium |
• Medium-term: Customers prefer to use low-carbon and green products (such as using green electricity); customers transfer orders to other brands, resulting in the risk of revenue reduction
• Long-term: Increased operating costs due to customer requests for increased green power |
Medium-term:
Actively invest in the development of high-end manufacturing processes, establish an industry with innovative technology and intellectual autonomy, and develop new products that are high-end, low-carbon and environmentally friendly to achieve the carbon reduction goals set by law
Long-term:
Planning the purchase of green electricity and assessing the installation of photovoltaic
|
• Medium-term: Reduced demand for goods and services due to shift in consumer preferences
• Long-term: The cost of green power and photovoltaics |
| Reputation |
Stigmatization of Sector |
Short-term |
|
Medium |
• The production process will produce pollutants, subject to government supervision |
Set energy-saving and high-efficiency equipment
Intelligent control to improve efficiency
Improving waste reuse
|
Reduction in capital availability |
Taiwan Facilities; Mainland China Facilities
Financial information of the Unimicron Climate Change Initiative
In 2022, the Company has already invested 0.06% of its annual revenue in energy-saving improvement and the purchase of energy-saving products in response to climate change.
From 2023 to 2026, We expect to invest NT$5.565 billion in energy-saving and carbon reduction improvement projects, green energy storage equipment, hydrogen fuel cell, etc.
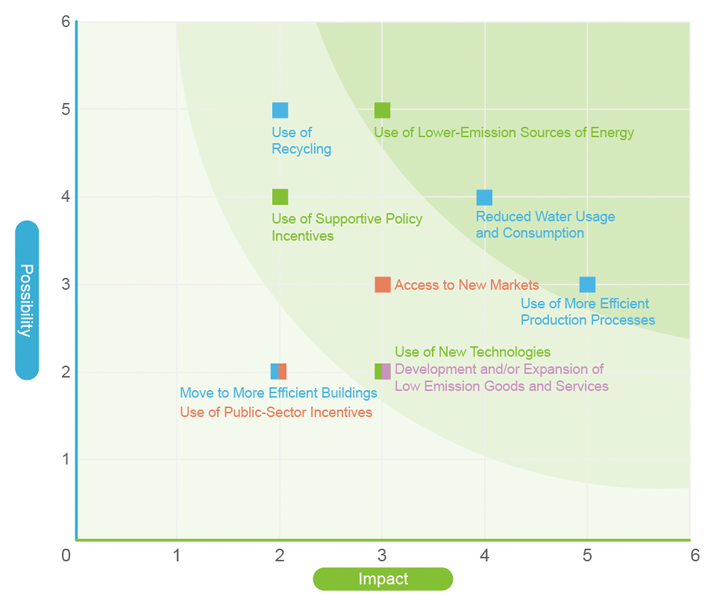
Opportunity Identification and Assessment
According to the results of the matrix analysis of climate change opportunities, the 3 most influential factors in response to climate change are reduced water usage and consumption, use of lower-emission sources of energy, and use of more efficient production processes. The next 5 items are the use of recycling, access to new markets, use of supportive policy incentives, use of new technologies, and development and/or expansion of low emission goods and services.
Unimicron Climate Change Opportunity Matrix
| Item |
Identified Opportunities |
Period |
Sites |
Level |
Impact |
Strategy |
Potential Financial Impact |
| Resource Efficiency |
Use of More Efficient Production Processes |
Long-term |
|
High |
- Reduce the defective rate of products to reduce the cost of scrapping
- Reduce the consumption of other chemical liquids to reduce the cost of chemical liquids.
|
Introduce circular economy thinking to reduce carbon emissions and use of energy resources.
Introduce new chemical liquids in electroplating process.
|
Reduced operating costs (e.g., through efficiency gains and cost reductions) |
| Reduced Water Usage and Consumption |
Short-term |
|
High |
- Improve water resource utilization efficiency and reduce dependence on raw water.
|
Recycle water from manufacturing, monitor the quality of recycled water, and divert and reuse it to related systems to continuously improve the recycling rate of water resources.
|
Promote circular economy and enhance customer satisfaction |
| Use of Recycling |
Short-term |
|
Medium |
- Reduce resource waste and mining, while creating circular economic value:
- Package ecycling: Carrier SBU has been advocating the use of recycled carriers since 2018.
- Use of gold salt material from gold recycling: PCB SBU Shanying Plant has introduced the use of gold salt made from recycled gold since 2021 and Luzhu Plant since 2022.
- Use of recycled copper materials: PCB SBU Shanying Plant and Luzhu II Plant will introduce it first in 2023.
|
Prioritize the purchase of reusable carriers, and for the Tray used in the shipment of carriers, the supplier will collect the carriers from the customer for reuse after shipment to the customer.
Introduce gold salts made from 100% recycled gold for use in related processes, and have the discharged gold waste recycled by the gold salt supplier to provide gold salts to Unimicron after re-refining.
Shanying Plant and Luzhu II Plant will be the first to introduce recycled copper
|
| Energy Source |
Use of Lower-Emission Sources of Energy |
Short-term |
|
High |
- Some of the boilers in the plant used to be fueled by fuel oil and diesel, etc., and gradually changed the fuel source to natural gas, which can effectively reduce the greenhouse gas emissions generated by burning fossil fuels.
|
Continuously replace high energy-consuming equipment, improve energy efficiency, and incorporate low-carbon energy-saving measures into the design of new plants.
We will continue to replace energy-consuming equipment and improve energy efficiency by 2025, and we plan to use renewable energy and solar photovoltaic facilities by 2030. We will continue to pay attention to the development of laws and policies to implement improvement plans to reduce carbon and save energy.
|
Reduced operational costs (e.g., through use of lowest cost abatement) |
| Use of Supportive Policy Incentives |
Long-term |
|
Medium |
- Invest in low-carbon energy improvements and apply for government subsidies.
|
Cooperate with the Industrial Development Bureau /TPCA Association to implement relevant low-carbon projects.
|
| Use of New Technologies |
Medium-term |
|
Medium |
- Medium-term: Strengthen the green environmental process by considering and designing the technical aspects of production to reduce the negative impact of production on the environment.
- Long-term: Introduce the use of hydrogen fuel cells for power generation to increase the diversity of power supply sources.
|
Medium-term:
Strengthen its investment in the development of new technologies and equipment through a tripartite model of joint development between industry, academia and research. For example, in 2022, the Company spent a total of NT$22.95 million on joint development with five universities, and the results of the development will be introduced one by one internally.
Long-term:
Install hydrogen fuel cells.
|
- Reduced operational costs (e.g., through use of lowest cost abatement)
- The benefits of investing in low carbon technologies
|
| Products and Services |
Development and/or Expansion of Low Emission Goods and Services |
Medium-term |
|
Medium |
- Expand into new markets and transform industries, and help reduce or adapt to the impact of global climate change risks through product or service innovation, strengthening market position and competitiveness.
|
In the future, products will be developed towards low-carbon, and it will be transformed to use renewable energy for production. Through quantitative data, immediacy and transparency, connect research and development, manufacturing, quality management and construction affairs and other units to establish a sustainable business ecosystem.
After the Strategic Marketing Department has formulated a low-carbon product development strategy for the year, the R&D Department will work with material suppliers to develop new low-carbon products according to the Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) process.
|
Increased revenue through demand for lower emissions products and services |
| Markets |
Access to New Markets |
Medium-term |
|
Medium |
- The investment in the coming year will still focus on improving the competitiveness of the PCB industry, supplemented by the reinforcement of existing investments, and new investments will be more cautious.
|
By cooperating with government administrative regulations and combining with the Group's core development strategy, effectively allocate the Group’s resources, implement the goal of low-carbon transformation, gain the recognition of new and regular customers, and increase the Group's revenue and profit.
|
Increased revenues through access to new and emerging markets (e.g., partnerships with governments, development banks) |
Taiwan Facilities; Mainland China Facilities
Climate Scenario Analysis
Scenario Analysis – Transition Risks
The Network for Greening the Financial System (NGFS) is a group of central banks and supervisors, that published its third version of climate change scenarios in September 2022, using the three scenarios of 2050 Net Zero (a policy target of 1.5˚C warming by the end of the century), NDCs and Current Policy. The three scenarios of 2050 Net Zero (policy target of 1.5˚C by the end of the century), NDCs, and Current Policy are used to assess the potential financial impacts of transition risks.
| Scenario |
Description |
Financial Implications |
| 2030 |
2050 |
| 2050 Net-Zero |
- Carbon price of US$95.48/tonne by 2030 and US$563.38/tonne by 2050 in Taiwan
- Carbon price of US$96.27/tonne by 2030 and US$689.91/tonne by 2050 in Mainland China
|
Percentage of Rrevenue: 2.75% |
Percentage of Revenue: 15.19% |
| Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) |
- Carbon price of US$0.41/tonne in Taiwan and Mainland China by 2030 and 2050
|
Percentage of Revenue: 0.01% |
Percentage of Revenue: 0.01% |
| Current Policy |
- Carbon price of US$0/tonne in Taiwan and Mainland China by 2030 and 2050
|
Percentage of Revenue: 0% |
Percentage of Revenue: 0% |
Note: The data of carbon price is based on NGFS Phase 3 Scenario Explorer.
Scenario Analysis – Physical Risks
Physical Risks uses NGFS’s scenario simulation of the current policy with a temperature increase of more than 3°C by the end of this century to assess the possible financial impact.
| Type |
Scenario Analysis |
Impact |
Strategies |
Financial Impact Assessment |
| Extreme Variability in Weather Patterns and Extreme Weather Events Such as Cyclones and Floods |
- For the risk of extreme rainfall and changes in rainfall patterns, Unimicron took into account the information published by the National Science and Technology Center for Disaster Reduction (NCDR) in the Climate Change and Disaster Risk Adaptation Platform to inventory the potential for flooding at each site and identify the level of flooding risk at each site. According to the estimated data, some of the plants are located in areas with accumulated rainfall of 600 mm or more in 24 hours, which is a flood disaster area during extreme rainfall or heavy rainfall.
- Meanwhile, according to the future climate trend of Taiwan, the total annual rainfall will increase by 8% and 15% in 2030 and 2050, respectively, under the worst case scenario of SSP5-8.5. The number of typhoons will decrease by about 15% and the proportion of severe typhoons will increase by about 100% during the century.
|
- The Guishan Plant is located in the area with potential 24-hour rainfall of 650 mm. The risk of flooding in Lujhu, Chungli, and Xinfeng areas is comparable to that of the base period (1976-2005) and the disaster risk level of 5 in most global climate models (2036~2065) under RCP8.5 scenarios, indicating that the disaster risk in this area is relatively high, which may lead to damage to plant and equipment and interruption of operations.
|
All factories, regardless of the level of disaster risk, have completed contingency drills according to the plan.
Strengthen the disaster resistance capacity of factory buildings in the Guishan area where the risk of flooding is relatively high.
Each plant will hold disaster prevention drills through internal management to reduce or avoid the possible impact of flooding in response to sudden natural disaster events.
|
- Historically, there have been no incidents of damage to equipment due to extreme rainfall at the sites of Unimicron Factories; enhanced measures have been taken to minimize disruption to operations or production at sites with relatively high risk of flooding.
- According to the scenario where the NGFS policy maintains the status quo, the impact assessment is estimated, and the estimated annual expected losses due to typhoons in Taiwan:
- By 2030, there will be increase of 2.6% compared to 2020.
- By 2050, there will be increase of 6.7% compared to 2020.
|
| Drought and Extreme Temperature Changes |
- In response to the risk of drought and extreme temperature change, the average annual temperature in Taiwan has increased by about 1.6°C over the past 110 years (1911-2020), and the temperature increase has accelerated in the past 50 and 30 years; the length of summer increased to about 120-150 days in the early 21st century, and the winter shortened to about 70 days; in recent years, the winter has shortened to about 20-40 days.
- With reference to the future climate trend projections for Taiwan, under the worst case scenario of SSP5-8.5, the annual average temperature will increase by more than 0.9˚C and 1.8˚C in 2030 and 2050, respectively; the number of days with extremely high temperatures above 36˚C will increase by about 6 days and 8.5 days in 2030 and 2050, respectively; and the number of days with maximum continuous rainfall will increase by about 2% and 12.4% in 2030 and 2050, respectively.
|
• The average temperature in summer has risen, and the probability of drought and water shortage has increased. |
Improve the efficiency of the air conditioning system and add inverters with control, reducing energy use and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
The emergency response water dispatch team is in charge of water trucks, water tanks, water sources, and other matters regarding water resources dispatching, to ensure uninterrupted operations.
Use of energy-saving and eco-label products
|
- According to the scenario where the NGFS policy maintains the status quo, the impact assessment is estimated, and the labor productivity caused by the heat wave in Taiwan:
- By 2030, there will be decrease of 0.7% compared to 2020.
- By 2050, there will be decrease of 1.9% compared to 2020.
- According to the highlights of IPCC AR6 Climate Science Report, Taiwan's future climate trend projection information estimates that:
- In 2030, the cost of emergency water purchase and increase in annual electricity consumption for air conditioning accounts for 0.179% of revenue.
- In 2050, the cost of emergency water purchase and increase in annual electricity consumption for air-conditioning accounts for 0.230% of revenue.
|